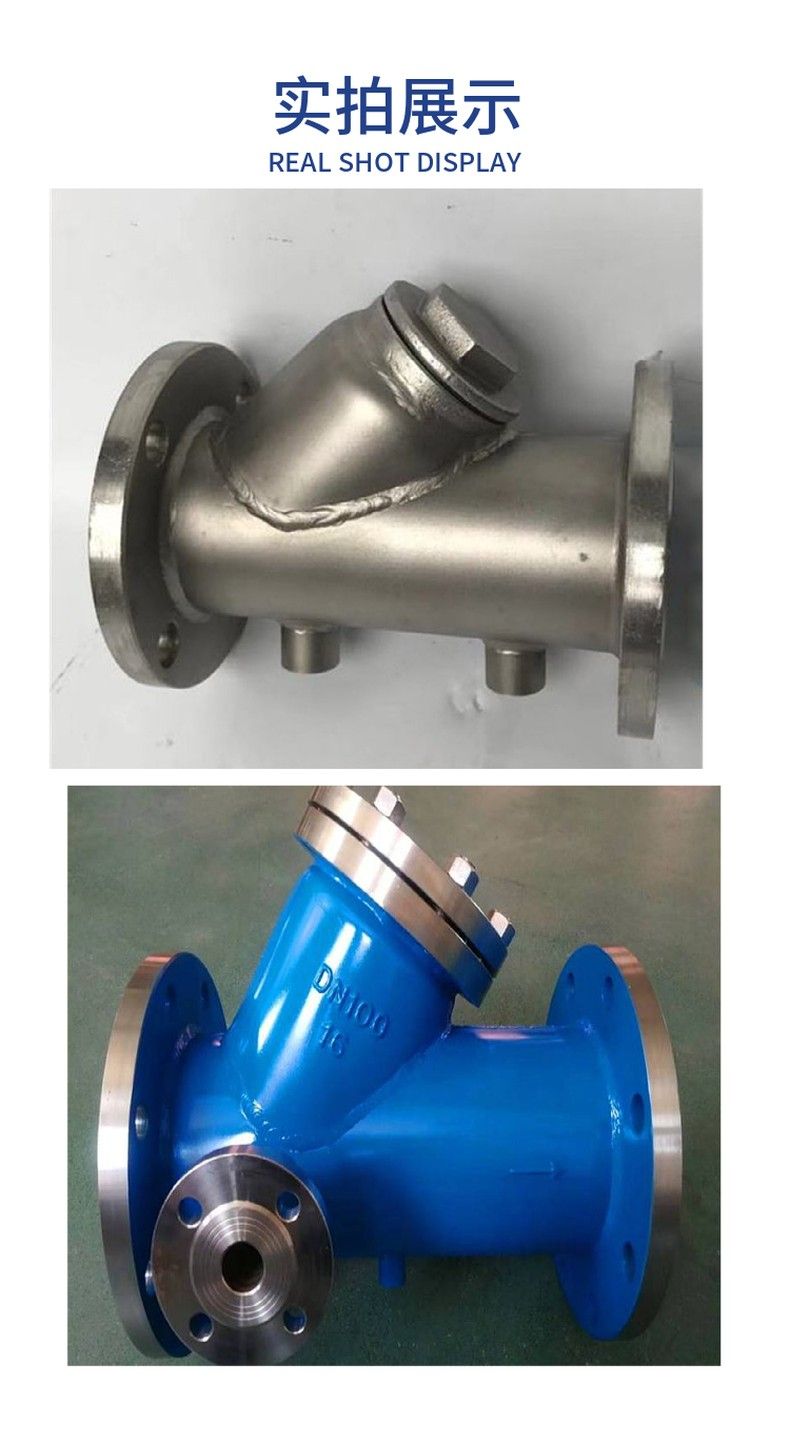
Thermal jacketed Y filter
The jacketed thermal insulation Y-type filter is based on the general Y-type filter, and the double-layer structure is made. The sandwich can pass through steam or heat conduction oil to maintain or improve the temperature of the fluid, prevent the fluid from solidifying, improve the filtration speed of the viscous liquid, or meet the temperature requirements of the next process. Jacketed filters are mostly used in areas with low temperatures.
Many liquids in order to obtain good transport performance, or because the temperature will crystallize or solidify, usually in the filtration of its heat preservation, in order to make the filtration easier or meet the next process of the temperature requirements, heat preservation filter is your filter. The middle layer can be thermally heated oil or steam heat preservation or refueling. Optimized for very good performance with precision casting mold top in filter structure. Made of 304/316L stainless steel, suitable for handling various acid and alkali liquids, solvents and neutral liquids; High grade design specifications are adopted to ensure sufficient corrosion allowance and good reliability. Smooth fluid pipeline design, low pressure loss, more energy saving; Excellent sealing design, with the ring mouth, to overcome the traditional filter of the side leakage. Fast opening design, easy maintenance.
Technical parameters
1. Sandwich design, liquid insulation;
2. Single flow 20/45m3/h;
3.304/316L stainless steel corrosion resistance;
4. Design, advanced filter:
5. High operating temperature 220ºC;
6. Smooth fluid pipeline design;
7. Low pressure loss, more energy saving;
8. Block all kinds of soft and hard particle impurities;
9. Precision casting mold, reliable sealing characteristics;
10. Fast opening design, easy maintenance;
11. Suitable for handling all kinds of liquids;
12. The height of the tripod is adjustable and the installation is flexible.
Application field
1, chemical, petrochemical production of weakly corrosive materials, such as: water, oil, ammonia, hydrocarbons, etc.
2. Corrosive materials in chemical production, such as caustic soda, soda ash, concentrated sulfuric acid, carbonic acid, aldehyde acid, etc.
3. Low temperature materials in refrigeration, such as liquid methane, liquid ammonia, liquid oxygen and various coolants.
4, food, pharmaceutical production of hygiene requirements of the material, such as: beer, drinks, syrup, etc.